- Home
- Services & Solutions
- Disaster Mitigation・Crisis Management・Climate Change Measurements
- Utilization of high-precision radar precipitation data
Services & Solutions
Utilization of high-precision radar precipitation data
Close Monitoring of Torrential Rainfall Using Highly Accurate Precipitation Radar Data while also Providing Consulting Services to Improve Disaster Mitigation Plans
Localized torrential rain can cause flooding and traffic disruptions over a small area in a short period of time, especially in the urban areas. However, many local governments and infrastructure companies still often use rain gauges to monitor heavy rainfall and hence overlook localized rainfall, due to the sparseness of rain gauge networks.
Currently, improvements in the accuracy of weather radar observations enable identifying localized torrential rainfall in real time. Especially in the urban areas where the observation conditions are favorable, the accuracy is such that it can be utilized for making decisions in disaster mitigation system. By using “XRAIN*1,” which is developed in a 250 m grid covering almost the entire country, along with Japan Weather Association’s (JWA)’s own precipitation forecasting*2, ‘area rainfall monitoring’ can be conducted to support the disaster mitigation responses for heavy rainfall and ensure that heavy rainfall events are not overlooked. Furthermore, we will review the thresholds for heavy rain in disaster mitigation plans (e.g., the disaster preparedness plans) and the control thresholds for roads and railways to align with the ‘area precipitation monitoring.’
High-precision radar precipitation data
Features
- Localized heavy rainfall can be monitored with high frequency intervals of 5 to 10 minutes by using average precipitation per area within a municipality, etc.
- Observed data from your rain gauges can be incorporated and used for heavy rainfall monitoring with more accurate analyzed precipitation*3.
- Consulting services to transition heavy rainfall monitoring from the ground rain gauges to precipitation radar information, as well as for the review of rainfall thresholds.
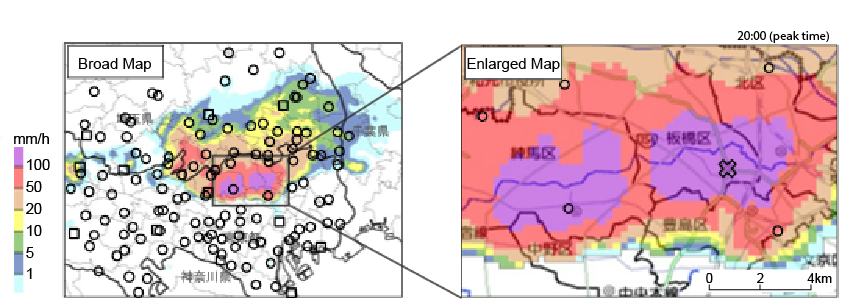
XRAIN Precipitation Map and Ground Rain Gauge Location Map
Left: Broad Map
Right: Enlarged Map of the Center of Heavy Rainfall
〇: The Rain Gauges Managed by Tokyo Metropolitan Government and Saitama Prefecture
□: The Rain Gauges Managed by Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
×: The Point in the Graph Below
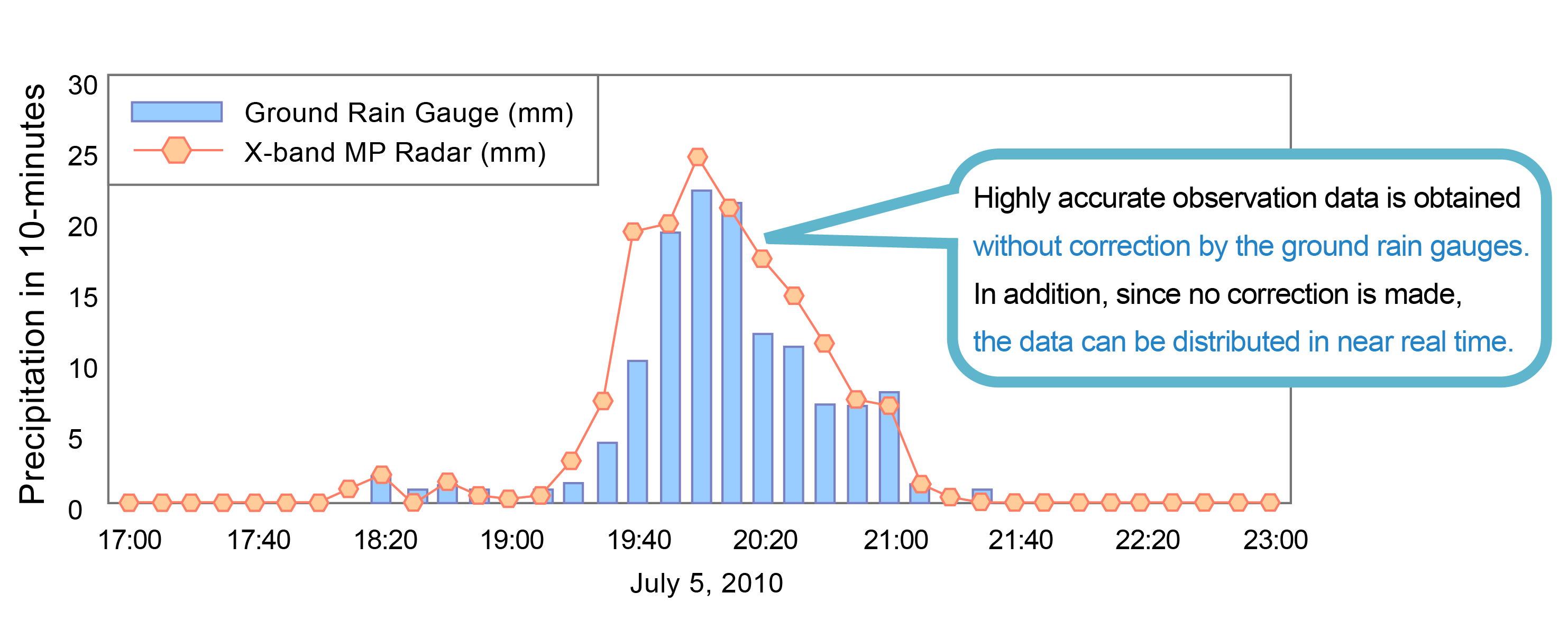
Accuracy Comparison of Observed Rainfall Values by XRAIN and the Ground Rain Gauge
* Comparison is made at the point marked with × in the upper right figure.
Ground rainfall data is utilized from the rain gauge observation values managed by the city office.
Recommended for those…
- Considering reviewing the regional disaster mitigation plans to ensure that they are aligned with the regional disaster characteristics.
(such as officials in charge of disaster mitigation in municipal and prefectural governments, etc.) - Considering reviewing the control criterion by precipitation by, leveraging the latest technology. (such as officials in charge of traffic control decisions at road and rail companies, etc.)
- Considering creating a new disaster mitigation plan that does not fail to detect localized heavy rainfall.
Terms
XRAIN (*1)
Observation network of “X-band MP Radar” and “C-band MP Radar”, which is managed by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT).
JWA’s own precipitation forecast (*2)
JWA’s own forecast information using XRAIN precipitation radar information.
Analyzed precipitation (*3)
The general “radar/rain gauge-analyzed precipitation by MLIT” is information of one-hour precipitation in 1 km grid, which is combined with data from the weather radar observations and data from the ground rain gauges of Japan Meteorological Agency, etc. JWA incorporates data from the customer-owned ground rain gauges to enhance accuracy, and provides 10-minute precipitation information.
Contact an expert for this service.
Services & Solutions Services & Solutions
-
Electric Power Demand Forecast
-

Solar Power Generation
-

Wind Power Generation
-

Environmental Impact Assessments
-

Disaster Mitigation・Crisis Management・Climate Change Measurements
-

Transport (Roads, Rails, Air, Oceans)
-
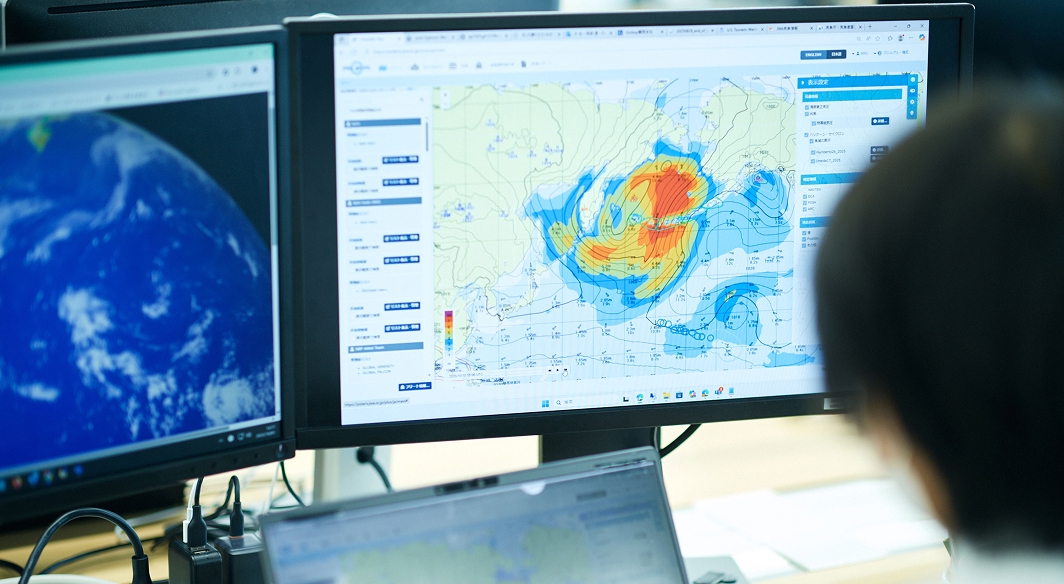

Meteorological and Oceanographic Forecasts & Real-Time Data Provisioning
-

Manufacturing, Retail, Advertising, and Marketing
-

tenki.jp & Media Services
-

Web, Apps and Other Services

