- Home
- Services & Solutions
- Disaster Mitigation・Crisis Management・Climate Change Measurements
- Investigation of optimal placement of rain gauge stations
Services & Solutions
Investigation of optimal placement of rain gauge stations
JWA investigates the optimal placement of rain gauge stations by analyzing both ground-based and radar rainfall data (Radar-Raingauge Analyzed Precipitation by Japan Meteorological Agency)
When observing rainfall with ground rain gauges, it is essential to install them in locations that provide high regional representativeness (covering a wider area) based on the rainfall scales and regional rainfall characteristics. To achieve this, we examine the representative coverage and blank areas of each rain gauge station and assess the regional representativeness of existing installations. We also suggest appropriate locations for rain gauges to fill blank areas, and in cases of significant overlap, recommend reducing or relocating rain gauges. This investigation facilitates cost-effective optimization of rain gauge placement.
Methodology:
The analysis of blank areas in rain gauge coverage is performed through correlation analysis of ground rain gauge data, such as customer-owned rain gauge data, the Automated Meteorological Data Acquisition System (AMeDAS) of the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), telemeters of the Japan Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, and radar-raingauge analyzed precipitation by JMA.
Features
Comprehensive data access: JWA possesses a database of historical AMeDAS rainfall and radar rainfall data, enabling swift and accurate investigations.
Effective disaster management: The optimal placement of rain gauges allows for more precise monitoring of heavy rainfall in target areas, contributing to effective disaster prevention measures such as flood and sediment disaster evacuation decisions and dam management.
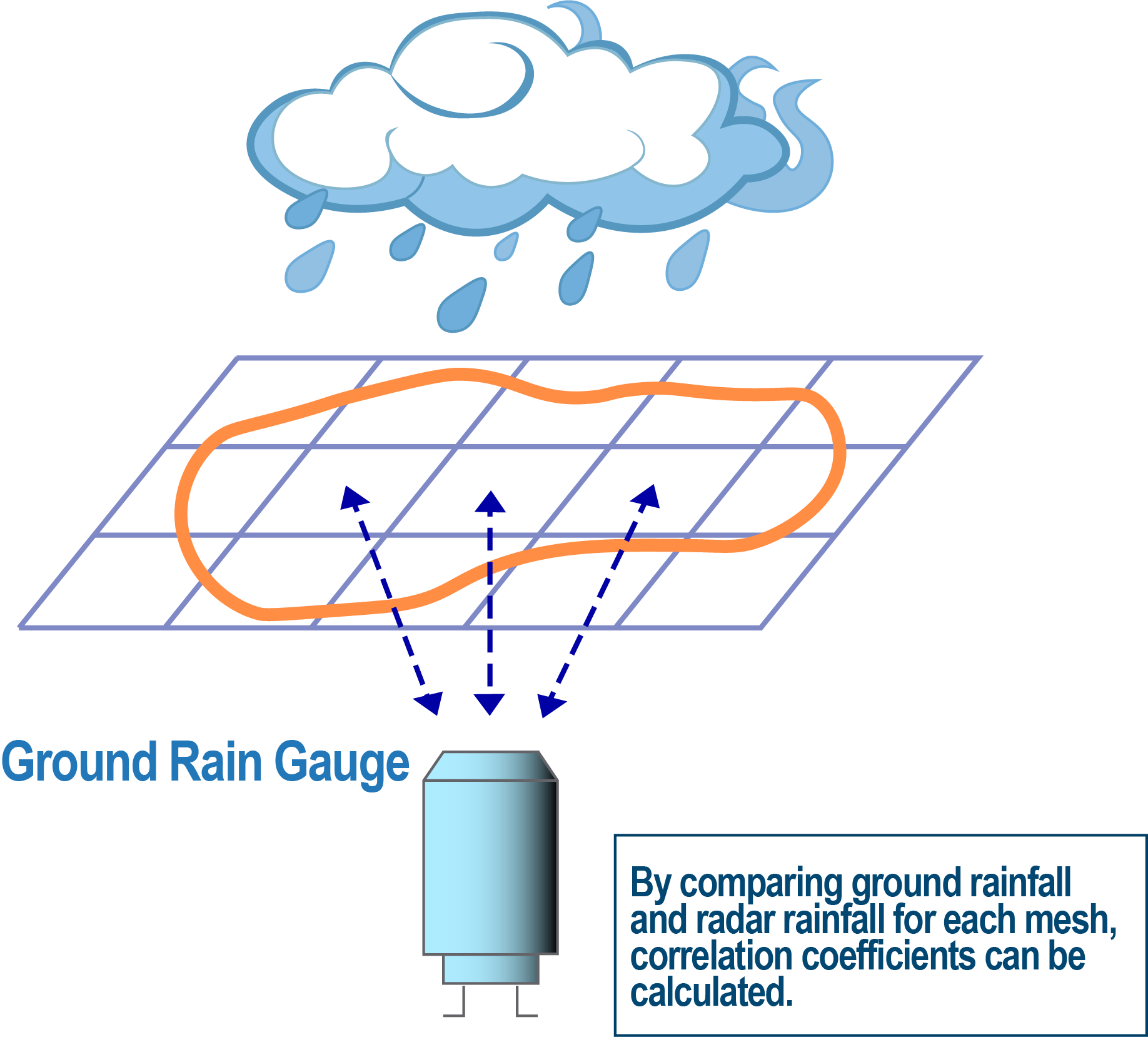
Image of correlation analysis
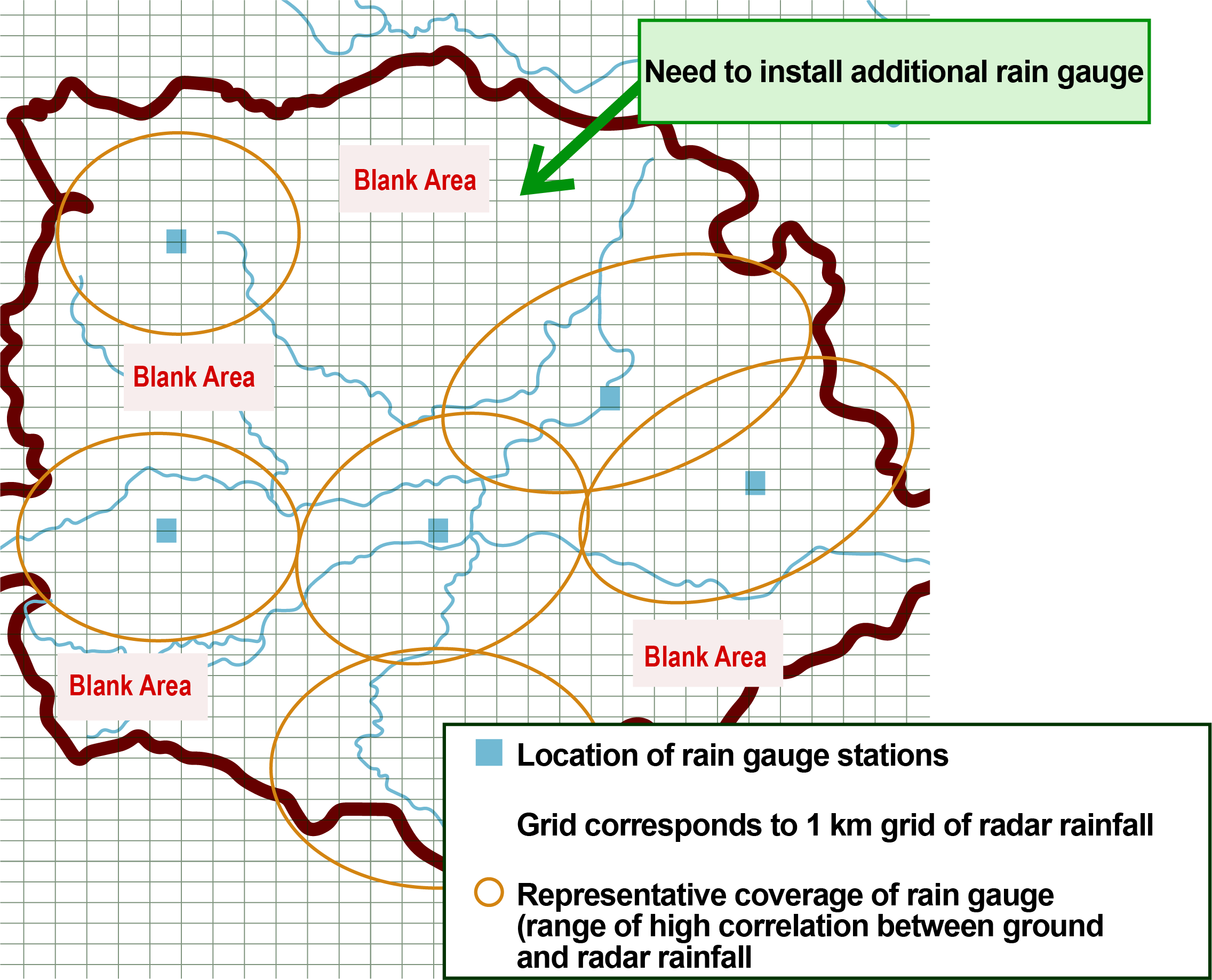
Image of blank area for study
Applications
- Planning: Develop plans for new installations and relocation of rain gauges
- Disaster Preparedness: Utilize data for monitoring heavy rainfall, managing dams, flood and sediment disaster alerts, and evacuation decision-making.
- Cost efficiency: Optimize the use of ground rain gauges and reduce costs by eliminating unnecessary gauges.
Terminology
Radar-raingauge analyzed precipitation by Japan Meteorological Agency: Precipitation distribution using a 1 km grid of hourly rainfall, updated every 10 minutes. It combines observed rainfall data from weather radars installed across Japan by the JMA with ground rain gauges such as AMeDAS. Using analyzed rainfall data allows for the detection of localized heavy rainfall that may not be captured by the rain gauge observation network. The JMA also uses it as a standard for issuing information on record-breaking short-duration heavy rainfall.
Contact an expert for this service.
Services & Solutions Services & Solutions
-
Electric Power Demand Forecast
-

Solar Power Generation
-

Wind Power Generation
-

Environmental Impact Assessments
-

Disaster Mitigation・Crisis Management・Climate Change Measurements
-

Transport (Roads, Rails, Air, Oceans)
-
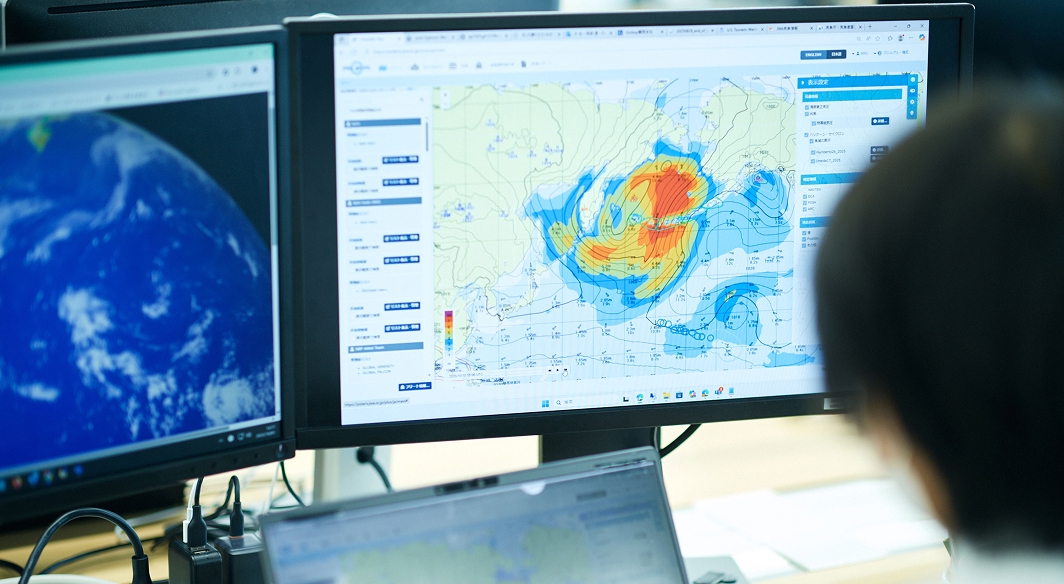

Meteorological and Oceanographic Forecasts & Real-Time Data Provisioning
-

Manufacturing, Retail, Advertising, and Marketing
-

tenki.jp & Media Services
-

Web, Apps and Other Services

